Breast Health Insights: Understanding Factors and Dietary Considerations
Breast health involves complex biological processes influenced by various factors. This article explores different elements that may affect breast tissue development and examines dietary patterns that some individuals find relevant when considering breast wellness. Understanding these aspects can contribute to more informed conversations with healthcare providers about comprehensive health strategies.
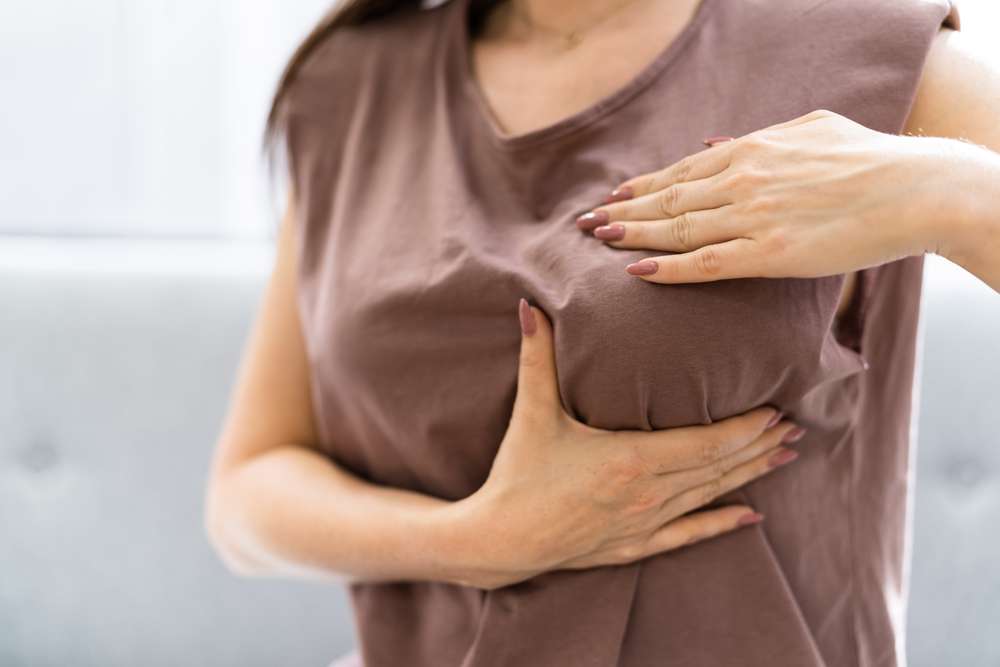

Breast health encompasses a wide range of considerations, from understanding risk factors to managing specific conditions through medical care and lifestyle adjustments. While advances in medical science have significantly improved outcomes, knowledge about prevention, early detection, and supportive care remains essential for individuals navigating these concerns.
What Is Breast Cancer and How Does It Develop?
Breast cancer occurs when cells in breast tissue begin to grow abnormally and uncontrollably. These cells can form tumors that may be benign or malignant. Malignant tumors have the potential to invade surrounding tissues or spread to other parts of the body through the lymphatic system or bloodstream. The disease can develop in various parts of the breast, including the ducts that carry milk to the nipple or the lobules that produce milk. Understanding the biological mechanisms behind cell mutation and growth helps medical professionals develop targeted interventions and helps patients understand their diagnosis.
What Treatment Options Are Available for Breast Cancer?
Medical interventions for breast cancer vary depending on the stage, type, and individual patient factors. Common approaches include surgical procedures to remove tumors or affected tissue, radiation therapy to target cancer cells, chemotherapy using medications to destroy cancer cells throughout the body, hormone therapy for hormone-receptor-positive cancers, and targeted drug therapies that attack specific characteristics of cancer cells. Treatment plans are highly individualized, often combining multiple approaches to achieve the best possible outcome. Medical teams typically include oncologists, surgeons, radiologists, and supportive care specialists who work together to develop comprehensive care strategies.
What Is Estrogen-Positive Breast Cancer?
Estrogen-positive breast cancer refers to tumors that have receptors for the hormone estrogen on their cell surfaces. These receptors allow estrogen to bind to cancer cells and fuel their growth. Approximately 70 percent of breast cancers are hormone-receptor-positive, making this a common subtype. Treatment for estrogen-positive breast cancer often includes hormone therapy designed to block estrogen production or prevent estrogen from attaching to cancer cells. Medications such as aromatase inhibitors and selective estrogen receptor modulators are frequently prescribed. Understanding hormone receptor status is crucial for determining the most effective treatment approach and predicting long-term outcomes.
What Are the Primary Causes of Breast Cancer?
The exact causes of breast cancer remain complex and multifactorial. Risk factors include genetic mutations, particularly in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, family history of breast or ovarian cancer, hormonal factors including early menstruation or late menopause, age, with risk increasing after 50, exposure to radiation, lifestyle factors such as alcohol consumption and obesity, and reproductive history including never having been pregnant or first pregnancy after age 30. While these factors increase risk, many individuals with multiple risk factors never develop breast cancer, and some with no known risk factors do. Research continues to explore the interplay between genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors in disease development.
What Foods Should Be Limited or Avoided for Breast Cancer Patients?
Dietary considerations play a supportive role in overall health during and after treatment. While no single food causes or cures breast cancer, certain dietary patterns may support better outcomes. Foods that patients are often advised to limit include processed meats due to preservatives and additives, refined sugars and carbohydrates which may contribute to inflammation, excessive alcohol which is linked to increased risk, foods high in saturated and trans fats, and heavily processed foods with artificial additives. Conversely, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is generally recommended. Nutritional guidance should be personalized, as treatment side effects may affect appetite, digestion, and nutritional needs. Consultation with registered dietitians who specialize in oncology can provide tailored recommendations.
| Food Category | Recommendation | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Processed Meats | Limit consumption | May contain carcinogenic preservatives |
| Refined Sugars | Reduce intake | Can promote inflammation and weight gain |
| Alcohol | Minimize or avoid | Linked to increased cancer risk |
| Saturated Fats | Moderate consumption | May contribute to obesity and inflammation |
| Whole Foods | Increase intake | Provide nutrients and antioxidants |
How Can Individuals Support Their Breast Health?
Proactive measures can contribute to overall breast health and early detection. Regular screening through mammograms and clinical examinations allows for early identification of abnormalities. Self-awareness about breast changes and promptly reporting concerns to healthcare providers is essential. Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced nutrition and regular physical activity may reduce risk. Limiting alcohol consumption and avoiding tobacco products supports overall health. For individuals with significant genetic risk, preventive measures such as enhanced surveillance or risk-reducing medications may be appropriate. Staying informed about personal risk factors and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers enables individuals to make educated decisions about their health.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
Understanding breast health involves recognizing risk factors, staying informed about available medical interventions, and adopting supportive lifestyle practices. While medical science continues to advance, individual awareness and proactive health management remain fundamental to positive outcomes. Each person’s journey is unique, requiring personalized medical guidance and comprehensive support from healthcare professionals.